Knee replacement
Ailments of the knee-joint, indication for surgery
The most frequent indication for knee replacement surgery is the age-related deterioration of the knee (ab arthrosis, osteoarthrosis). In small proportion it is also performed in cases of other diseases (PCP – polyarthritis chronica progressive – rheumatoid arthritis) or knee injuries or deformations caused by accidents.
The knee implant has to types: partial (UKA – unicompartmental arthroplasty) and total knee implant (TKR – total knee replacement).
The serious results achieved in the field of knee implantation during the last 25 years greatly improved the success rate of the outcome of surgeries of this kind. One of these improvement, was the re-introduction of the resurfacing (or partial) prosthesis implantation to knee surgery practice. This kind of implantation is less burdensome to the patient than total knee replacement.
The resurfacing prosthesis supplements the deteriorated surfaces of the femur and the tibia in only one part of the knee (usually the inner part). It is also called sledge prosthesis, since the metal component implanted on the femur resembles a sledge. The surgery replaces only the part of the joint most damaged by arthritis. This can be of immense importance, mainly in cases of younger patients, should the implant itself need a replacement because of its deterioration. The smaller the part of the joint we are forced to remove during the first surgery, the easier to replace the implant in the future if necessary.
Resurfacing (partial, sledge) knee prosthesis
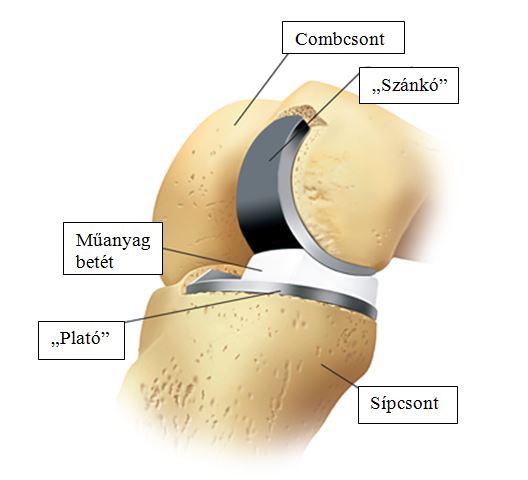
Total knee replacement replaces the whole knee joint surface, which means the femur joint surface and the tibia joint surface. These damaged and deteriorated joint surfaces are cut out completely, after which metal knee implant components are being implanted – usually anchored with bone cement - into the femur and the tibia. Between the two metal knee implant components a plastic sliding surface (insert) is placed. With the implantation of inserts of different thickness the tightness of the knee joint can be adjusted during knee replacement surgery.
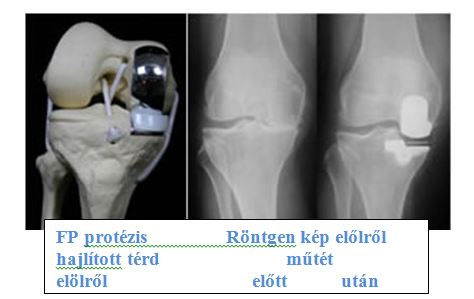
Types of knee implants
There are two basic types of prosthesis implantation:
- Cemented (glued) prosthesis implantation
- Uncemented (glueless) prosthesis implantation
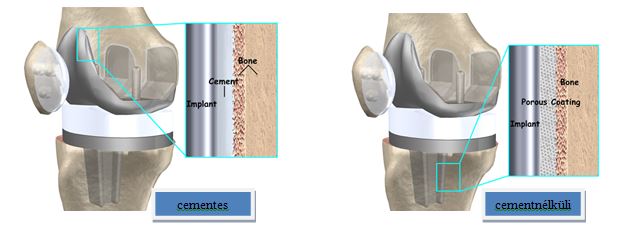
Both procedures are being used generally, in cases they combine the two, but in Hungary the prevalent technique is the cemented method. The decision - of which method should be used- is decided by the surgeon who considers the age and lifestyle of the patient, and the relevant experience gained in cases similar to the given patient.
Both implants are consisting of two main parts
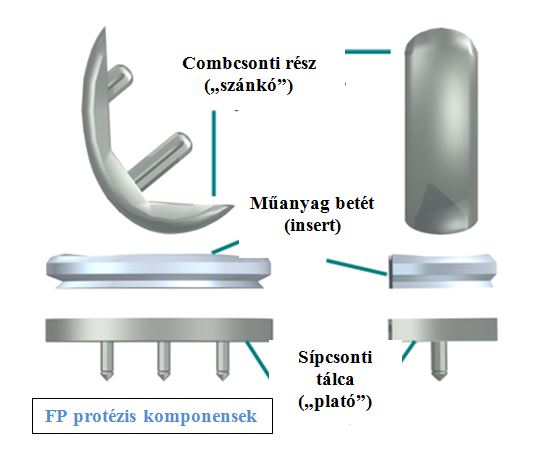
The tibial component of the prosthesis is to cover the top of the lower bone (the tibia) of the joint, while the femoral component is to cover the lower surface of the upper bone (the femur) of the joint, the femoral condyle.
The femoral component is made of metal, while the tibial component usually consists of two parts: a metal plate, which is fixed directly to the bone, and a plastic insert providing sliding surface (although we use types without metal plates as well). This plastic layer is so hard and slippery that you could even ice skate on it. It would endure that as well.
During the cemented procedure the metal (plastic) is fixed to the bone with the help of a special, two-component adhesive (bone cement). The uncemented procedure uses prostheses whit small holes on their surface (special porous cover), through which the bone literally grows into the metal, thus fixing it to the right position.
What happens during surgery?
Prior to surgery a physical and medical imaging examination takes place, while routine blood and urine examinations are performed in order to exclude the possibility of infection. The patient receives anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory medication.
The knee replacement surgery usually transpires over 2-3 hours. During surgery the end of the femur is removed along an approximately 20 cm long incision, and replaced with a metal jacket, while the end of the tibia is substituted with a prosthesis equipped with a metal stem. After this a plastic surface is placed between them, which will help adjusting the tightness of the knee joint. Depending on the state of the kneecap, a plastic “button” can be implanted to the place of the kneecap to substitute it. The posterior cruciate ligament is a tissue, which stabilizes both sides of the knee joint. During knee replacement surgery this ligament is either stays in place or gets substituted with polyethylene.
The prosthesis is usually fixed with bone cement and has a lifetime of more than 10 years, after which it needs replacement. At the end of the surgery a drain tube is added, which is used to remove possible hematoma.
Post-operative rehabilitation
The success of the surgery is greatly influenced by post-operative physiotherapy. The delayed start of knee movements can cause serious joint disabilities, therefore the most important task is the early and regular moving of the knee. A couple of days later when scar pains lessens, active knee joint exercises are introduced in a relieved state. The learning and regular execution of these exercises makes the replaced knee joint mobile and painless.
Post-operative physiotherapy is adjusted to the general and physical state of the patient where possible.
The goal of the physiotherapist during the first couple of days after the surgery:
Preventing complications with vein and breathing exercises, and preparing for quick and safe mobilization with strengthening the muscles and exercising the joints of the operated limb.
Rehabilitation plays an important role in the knee prosthesis program provided by the partner clinic of Smart Choice Medical Travel, where the patients can gradually return to active life with the help of an experienced medical staff in 20 days. The program includes daily physician-controlled personalized physiotherapy, circulation improving exercises and relaxing and therapeutic massages.
There are a couple of rules, which has to be adhered to during physiotherapy as well as everyday movements in order to protect the stability of the joint. These guidelines are presented by the physiotherapist, who also teaches the movements, so risky situations can be avoided.
Before leaving the hospital the patient learns those exercises, which he/she has to do regularly over the first six weeks after the operation.
Should you have any additional question, please feel free to Contact Us.
Check our Hip Replacement Program Read FAQ about orthopaedic treatments